We are calling for the world’s best AI Engineer talks for AI Architects, /r/localLlama, Model Context Protocol (MCP), GraphRAG, AI in Action, Evals, Agent Reliability, Reasoning and RL, Retrieval/Search/RecSys , Security, Infrastructure, Generative Media, AI Design & Novel AI UX, AI Product Management, Autonomy, Robotics, and Embodied Agents, Computer-Using Agents (CUA), SWE Agents, Vibe Coding, Voice, Sales/Support Agents at AIEWF 2025! Fill out the 2025 State of AI Eng survey for $250 in Amazon cards and see you from Jun 3-5 in SF!
Coreweave’s now-successful IPO has led to a lot of questions about the GPU Neocloud market, which Dylan Patel has written extensively about on SemiAnalysis. Understanding markets requires an interesting mix of technical and financial expertise, so this will be a different kind of episode than our usual LS domain.
When we first published $2 H100s: How the GPU Rental Bubble Burst, we got 2 kinds of reactions on Hacker News:
“Ah, now the AI bubble is imploding!”
“Duh, this is how it works in every GPU cycle, are you new here?”
We don’t think either reaction is quite right. Specifically, it is not normal for the prices of one of the world’s most important resources right now to swing from $1 to $8 per hour based on drastically inelastic demand AND supply curves - from 3 year lock-in contracts to stupendously competitive over-ordering dynamics for NVIDIA allocations — especially with increasing baseline compute needed for even the simplest academic ML research and for new AI startups getting off the ground.
We’re fortunate today to have Evan Conrad, CEO of SFCompute, one of the most exciting GPU marketplace startups, talk us through his theory of the economics of GPU markets, and why he thinks CoreWeave and Modal are well positioned, but Digital Ocean and Together are not.
However, more broadly, the entire point of SFC is creating liquidity between GPU owners and consumers and making it broadly tradable, even programmable:
As we explore, these are the primitives that you can then use to create your own, high quality, custom GPU availability for your time and money budget, similar to how Amazon Spot Instances automated the selective buying of unused compute.
The ultimate end state of where all this is going is GPU that trade like other perishable, staple commodities of the world - oil, soybeans, milk. Because the contracts and markets are so well established, the price swings also are not nearly as drastic, and people can also start hedging and managing the risk of one of the biggest costs of their business, just like we have risk-managed commodities risks of all other sorts for centuries. As a former derivatives trader, you can bet that swyx doubleclicked on that…
Show Notes
Full Video Pod
Timestamps
[00:00:05] Introductions
[00:00:12] Introduction of guest Evan Conrad from SF Compute
[00:00:12] CoreWeave Business Model Discussion
[00:05:37] CoreWeave as a Real Estate Business
[00:08:59] Interest Rate Risk and GPU Market Strategy Framework
[00:16:33] Why Together and DigitalOcean will lose money on their clusters
[00:20:37] SF Compute's AI Lab Origins
[00:25:49] Utilization Rates and Benefits of SF Compute Market Model
[00:30:00] H100 GPU Glut, Supply Chain Issues, and Future Demand Forecast
[00:34:00] P2P GPU networks
[00:36:50] Customer stories
[00:38:23] VC-Provided GPU Clusters and Credit Risk Arbitrage
[00:41:58] Market Pricing Dynamics and Preemptible GPU Pricing Model
[00:48:00] Future Plans for Financialization?
[00:52:59] Cluster auditing and quality control
[00:58:00] Futures Contracts for GPUs
[01:01:20] Branding and Aesthetic Choices Behind SF Compute
[01:06:30] Lessons from Previous Startups
[01:09:07] Hiring at SF Compute
Transcript
Alessio [00:00:05]: Hey everyone, welcome to the Latent Space podcast. This is Alessio, partner and CTO at Decibel, and I'm joined by my co-host Swyx, founder of Smol AI.
Swyx [00:00:12]: Hey, and today we're so excited to be finally in the studio with Evan Conrad from SF Compute. Welcome. I've been fortunate enough to be your friend before you were famous, and also we've hung out at various social things. So it's really cool to see that SF Compute is coming into its own thing, and it's a significant presence, at least in the San Francisco community, which of course, it's in the name, so you couldn't help but be.
Evan: Indeed, indeed. I think we have a long way to go, but yeah, thanks.
Swyx: Of course, yeah. One way I was thinking about kicking on this conversation is we will likely release this right after CoreWeave IPO. And I was watching, I was looking, doing some research on you. You did a talk at The Curve. I think I may have been viewer number 70. It was a great talk. More people should go see it, Evan Conrad at The Curve. But we have like three orders of magnitude more people. And I just wanted to, to highlight, like, what is your analysis of what CoreWeave did that went so right for them?
Evan: Sell locked-in long-term contracts and don't really do much short-term at all. I think like a lot of people had this assumption that GPUs would work a lot like CPUs and the like standard business model of any sort of CPU cloud is you buy commodity hardware, then you lay on services that are mostly software, and that gives you high margins and pretty much all your value comes from those services. Not really the underlying. Compute in any capacity and because it's commodity hardware and it's not actually that expensive, most of that can be sort of on-demand compute. And while you do want locked-in contracts for folks, it's mostly just a sort of de-risk situation. It helps you plan revenue because you don't know if people are going to scale up or down. But fundamentally, people are like buying hourly and that's how your business is structured and you make 50 percent margins or higher. This like doesn't really work in GPUs. And the reason why it doesn't work is because you end up with like super price sensitive customers. And that isn't because necessarily it's just way more expensive, though that's totally the case. So in a CPU cloud, you might have like, you know, let's say if you had a million dollars of hardware in GPUs, you have a billion dollars of hardware. And so your customers are buying at much higher volumes than you otherwise expect. And it's also smaller customers who are buying at higher amounts of volume. So relative to what they're spending in general. But in GPUs in particular, your customer cares about the scaling law. So if you take like Gusto, for example, or Rippling or an HR service like this, when they're buying from an AWS or a GCP, they're buying CPUs and they're running web servers, those web servers, they kind of buy up to the capacity that they need, they buy enough, like CPUs, and then they don't buy any more, like, they don't buy any more at all. Yeah, you have a chart that goes like this and then flat. Correct. And it's like a complete flat. It's not even like an incremental tiny amount. It's not like you could just like turn on some more nodes. Yeah. And then suddenly, you know, they would make an incremental amount of money more, like Gusto isn't going to make like, you know, 5% more money, they're gonna make zero, like literally zero money from every incremental GPU or CPU after a certain point. This is not the case for anyone who is training models. And it's not the case for anyone who's doing test time inference or like inference that has scales at test time. Because like you, your scaling laws mean that you may have some diminishing returns, but there's always returns. Adding GPUs always means your model does actually get. And that actually does translate into revenue for you. And then for test time inference, you actually can just like run the inference longer and get a better performance. Or maybe you can run more customers faster and then charge for that. It actually does translate into revenue. Every incremental GPU translates to revenue. And what that means from the customer's perspective is you've got like a flat budget and you're trying to max the amount of GPUs you have for that budget. And it's very distinctly different than like where Augusto or Rippling might think, where they think, oh, we need this amount of CPUs. How do we, you know, reduce that? How do we reduce our amount of money that we're spending on this to get the same amount of CPUs? What that translates to is customers who are spending in really high volume, but also customers who are super price sensitive, who don't give a shit. Can I swear on this? Can I swear? Yeah. Who don't give a shit at all about your software. Because a 10% difference in a billion dollars of hardware is like $100 million of value for you. So if you have a 10% margin increase because you have great software, on your billion, the customers are that price sensitive. They will immediately switch off if they can. Because why wouldn't you? You would just take that $100 million. You'd spend $50 million on hiring a software engineering team to replicate anything that you possibly did. So that means that the best way to make money in GPUs was to do basically exactly what CoreWeave did, which is go out and sign only long-term contracts, pretty much ignore the bottom end of the market completely, and then maximize your long-term contracts. With customers who don't have credit risk, who won't sue you, or are unlikely to sue you for frivolous reasons. And then because they don't have credit risk and they won't sue you for frivolous reasons, you can go back to your lender and you can say, look, this is a really low risk situation for us to do. You should give me prime, prime interest rate. You should give me the lowest cost of capital you possibly can. And when you do that, you just make tons of money. The problem that I think lots of people are going to talk about with CoreWeave is it doesn't really look like a cloud platform. It doesn't really look like a cloud provider financially. It also doesn't really look like a software company financially.
Swyx [00:05:37]: It's a bank.
Evan [00:05:38]: It's a bank. It's a real estate company. And it's very hard to not be that. The problem of that that people have tricked themselves into is thinking that CoreWeave is a bad business. I don't think CoreWeave is explicitly a bad business. There's a bunch of people, there's kind of like two versions of the CoreWeave take at the moment. There's, oh my God, CoreWeave, amazing. CoreWeave is this great new cloud provider competitive with the hyperscalers. And to some extent, this is true from a structural perspective. Like, they are indeed a real sort of thing against the cloud providers in this particular category. And the other take is, oh my gosh, CoreWeave is this horrible business and so on and blah, blah, blah. And I think it's just like a set of perception or perspective. If you think CoreWeave's business is supposed to look like the traditional cloud providers, you're going to be really upset to learn that GPUs don't look like that at all. And in fact, for the hyperscalers, it doesn't look like this either. My intuition is that the hyperscalers are probably going to lose a lot of money, and they know they're going to lose a lot of money on reselling NVIDIA GPUs, at least. Hyperscalers, but I want to, Microsoft, AWS, Google. Correct, yeah. The Microsoft, AWS, and Google. Does Google resell? I mean, Google has TPUs. Google has TPUs, but I think you can also get H100s and so on. But there are like two ways they can make money. One is by selling to small customers who aren't actually buying in any serious volume. They're testing around, they're playing around. And if they get big, they're immediately going to do one of two things. They're going to ask you for a discount. Because they're not going to pay your crazy sort of margin that you have locked into your business. Because for CPUs, you need that. They're going to pay your massive per hour price. And so they want you to sign a long-term contract. And so that's your other way that you can make money, is you can basically do exactly what CoreWeave does, which is have them pay as much as possible upfront and lock in the contract for a long time. Or you can have small customers. But the problem is that for a hyperscaler, the GPUs to... To sell on the low margins relative to what your other business, your CPUs are, is a worse business than what you are currently doing. Because you could have spent the same money on those GPUs. And you could have trained model and you could have made a model on top of it and then turn that into a product and had high margins from your product. Or you could have taken that same money and you could have competed with NVIDIA. And you could have cut into their margin instead. But just simply reselling NVIDIA GPUs doesn't work like your CPU business. Where you're able to capture high margins from big customers and so on. And then they never leave you because your customers aren't actually price sensitive. And so they won't switch off if your prices are a little higher. You actually had a really nice chart, again, on that talk of this two by two. Sure. Of like where you want to be. And you also had some hot takes on who's making money and who isn't.
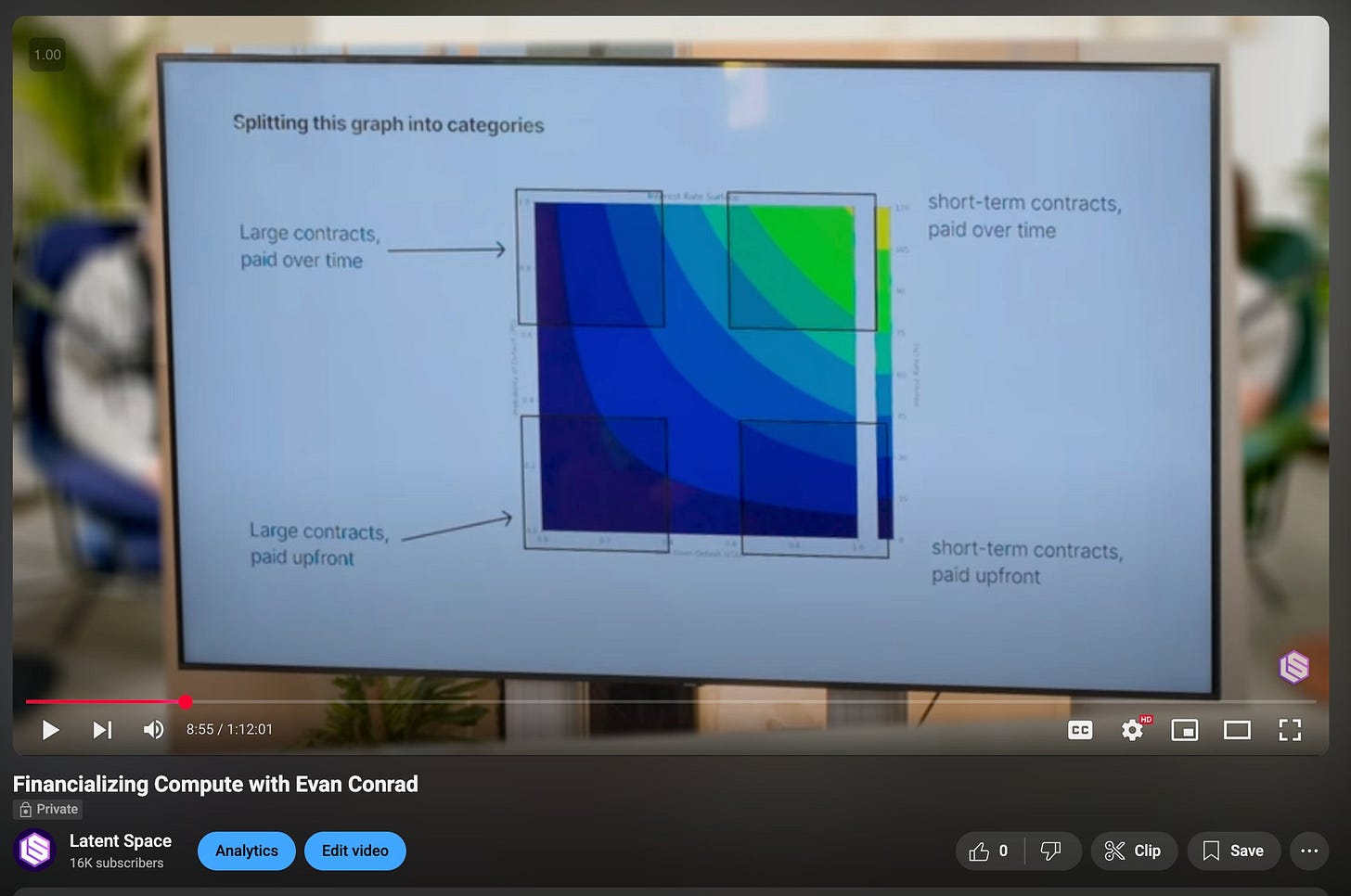
Swyx: So CoreUv locked up long-term contracts. Get that. Yes. Maybe share your mental framework. Just verbally describe it because we're trying to help the audio listeners as well. Sure. People can look up the chart if they want to.
Evan: Sure. Okay. So this is a graph of interest rates. And on the y-axis, it's a probability you're able to sell your GPUs from zero to one. And on the x-axis, it's how much they'll depreciate in cost from zero to one. And then you had ISO cost curves or ISO interest rate curves. Yeah. So they kind of shape in a sort of concave fashion. Yeah. The lowest interest rates enable the most aggressive. form of this cost curve. And the higher interest rates go, the more you have to push out to the top right. Yeah. And then you had some analysis of where every player sits in this, including CoreUv, but also Together and Modal and all these other guys. I thought that was super insightful. So I just wanted to elaborate. Basically, it's like a graph of risk and the genres of places where you can be and what the risk is associated with that. The optimal thing for you to do, if you can, is to lock in long-term contracts that are paid all up front or in with a situation in which you trust the other party to pay you over time. So if you're, you know, selling to Microsoft or something or OpenAI. Which are together 77% of the revenue of CoreUv. Yeah. So if you're doing that, that's a great business to be in because your interest rate that you can pitch for is really low because no one thinks Microsoft is going to default. And like maybe OpenAI will default, but the backing by Microsoft kind of doesn't. And I think there's enough, like, generally, it looks like OpenAI is winning that you can make it's just a much better case than if you're selling to the pre-seed startup that just raised $30 million or something pre-revenue. It's like way easier to make the case that the OpenAI is not going to default than the pre-seed startup. And so the optimal place to be is selling to the maximally low risk customer for as long as possible. And then you never have to worry about depreciation and you make lots of money. The less. Good. Good place to be is you could sell long-term contracts to people who might default on you. And then if you're not bringing it to the present, so you're not like saying, hey, you have to pay us all up front, then you're in this like more risky territory. So is it top left of the chart? If I have the chart right, maybe. Large contracts paid over time. Yeah. Large contracts paid over time is like top left. So it's more risky, but you could still probably get away with it. And then the other opportunity is that you could sell short-term contracts for really high prices. And so lots of people tried that too, because this is actually closer to the original business model that people thought would work in cloud providers for CPUs. It works for CPUs, but it doesn't really work for GPUs. And I don't think people were trying this because they were thinking about the risk associated with it. I think a lot of people are just come from a software background, have not really thought about like cogs or margins or inventory risk or things that you have to worry about in the physical world. And I think they were just like copy pasting the same business model onto CPUs. And also, I remember fundraising like a few years ago. And I know based on. Like what we knew other people were saying who were in a very similar business to us versus what we were saying. And we know that our pitch was way worse at the time, because in the beginning of SF Compute, we looked very similar to pretty much every other GPU cloud, not on purpose, but sort of accidentally. And I know that the correct pitch to give to an investor was we will look like a traditional CPU cloud with high margins and we'll sell to everyone. And that is a bad business model because your customers are price sensitive. And so what happens is if you. Sell at high prices, which is the price that you would need to sell it in order to de-risk your loss on the depreciation curve, and specifically what I mean by that is like, let's say you're selling it like $5 an hour and you're paying $1.50 an hour for the GPU under the hood. It's a little bit different than that, but you know, nice numbers, $5 an hour, $1.50 an hour. Great. Excellent. Well, you're charging a really high price per GPU hour because over time the price will go down and you'll get competed out. And what you need is to make sure that you never go under, or if you do go under your underlying cost. You've made so much money in the first part of it that the later end of it, like doesn't matter because from the whole structure of the deal, you've made money. The problem is that just, you think that you're going to be able to retain your customers with software. And actually what happens is your customers are super price sensitive and push you down and push you down and push you down and push you down, um, that they don't care about your software at all. And then the other problem that you have is you have, um, really big players like the hyperscalers who are looking to win the market and they have way more money than you, and they can push down on margin. Much better than you can. And so if they have to, and they don't, they don't necessarily all the time, um, I think they actually keep pride of higher margin, but if they needed to, they could totally just like wreck your margin at any point, um, and push you down, which meant that that quadrant over there where you're charging a high price, um, and just to make up for the risk completely got destroyed, like did not work at all for many places because of the price sensitivity, because people could just shove you down instead that pushed everybody up to the top right-hand corner of that, which is selling short-term. Contracts for low prices paid over time, which is the worst place to be in, um, the worst financial place to be in because it has the highest interest rate, um, which means that your, um, your costs go up at the same time, your, uh, your incoming cash goes down and squeezes your margins and squeezes your margins. The nice thing for like a core weave is that most of their business is over on the, on the other sides of those quadrants that the ones that survive. The only remaining question I have with core weave, and I promise I get to ask if I can compute, and I promise this is relevant to SOF Compute in general, because the framework is important, right? Sure. To understand the company. So why didn't NVIDIA or Microsoft, both of which have more money than core weave, do core weave, right? Why didn't they do core weave? Why have this middleman when either NVIDIA or Microsoft have more money than God, and they could have done an internal core weave, which is effectively like a self-funding vehicle, like a financial instrument. Why does there have to be a third party? Your question is like... Why didn't Microsoft, or why didn't NVIDIA just do core weave? Why didn't they just set up their own cloud provider? I think, and I don't know, and so correct me if I'm wrong, and lots of people will have different opinions here, or I mean, not opinions, they'll have actual facts that differ from my facts. Those aren't opinions. Those are actually indeed differences of reality, is that NVIDIA doesn't want to compete with their customers. They make a large amount of money by selling to existing clouds. If they launched their own core weave, then it would be a lot more money. It'd make it much harder for them to sell to the hyperscalers, and so they have a complex relationship with there. So not great for them. Second is that, at least for a while, I think they were dealing with antitrust concerns or fears that if they're going through, if they own too much layers of the stack, I could imagine that could be a problem for them. I don't know if that's actually true, but that's where my mind would go, I guess. Mostly, I think it's the first one. It's that they would be competing directly with their primary customers. Then Microsoft could have done it, right? That's the other question. Yeah, so Microsoft didn't do it. And my guess is that... NVIDIA doesn't want Microsoft to do it, and so they would limit the capacity because from NVIDIA's perspective, both they don't want to necessarily launch their own cloud provider because it's competing with their customers, but also they don't want only one customer or only a few customers. It's really bad for NVIDIA if you have customer concentration, and Microsoft and Google and Amazon, like Oracle, to buy up your entire supply, and then you have four or five customers or so who pretty much get to set prices. Monopsony. Yeah, monopsony. And so the optimal thing for you is a diverse set of customers who all are willing to pay at whatever price, because if you don't, somebody else will. And so it's really optimal for NVIDIA to have lots of other customers who are all competing against each other. Great. Just wanted to establish that. It's unintuitive for people who have never thought about it, and you think about it all day long. Yeah.
Swyx: The last thing I'll call out from the talk, which is kind of cool, and then I promise we'll get to SF Compute, is why will DigitalOcean and Together lose money on their clusters? Why will DigitalOcean and Together lose money on their clusters?
Evan [00:16:33]: I'm going to start by clarifying that all of these businesses are excellent and fantastic. That Together and DigitalOcean and Lambda, I think, are wonderful businesses who build excellent products. But my general intuition is that if you try to couple the software and the hardware together, you're going to lose money. That if you go out and you buy a long-term contract from someone and then you layer on services, or you buy the hardware yourself and you spin it up and you get a bunch of debt, you're going to run into the same problem that everybody else did, the same problem we did, same problem the hyperscalers did. And that's exactly what the hyperscalers are doing, which is you cannot add software and make high margins like a cloud provider can. You can pitch that into investors and it will totally make sense, and it's like the correct play in CPUs, but there isn't software you could make to make this occur. If you're spending a billion dollars on hardware, you need to make a billion dollars of software. There isn't a billion dollars of software that you can realistically make, and if you do, you're going to look like SAP. And that's not a knock on SAP. SAP makes a fuck ton of money, right? Right. Right. Right. Right. There aren't that many pieces of software that you could make, that you can realistically sell, like a billion dollars of software, and you're probably not going to do it to price-sensitive customers who are spending their entire budget already on compute. They don't have any more money to give you. It's a very hard proposition to do. And so many parties have been trying to do this, like, buy their own compute, because that's what a traditional cloud does. It doesn't really work for them. You know that meme where there's, like, the Grim Reaper? And he's, like, knocking on the door, and then he keeps knocking on the next door? We have just seen door after door after door of the Grim Reeker comes by, and the economic realities of the compute market come knocking. And so the thing we encourage folks to do is if you are thinking about buying a big GPU cluster and you are going to layer on software on top, don't. There are so many dead bodies in the wake there. We would recommend not doing that. And we, as SF Compute, our entire business is structured to help you not do that. It's helped disintegrate these. The GPU clouds are fantastic real estate businesses. If you treat them like real estate businesses, you will make a lot of money. The cloud services you can make on that, all the software you want to make on that, you can do that fantastically. If you don't own the underlying hardware, if you mix these businesses together, you get shot in the head. But if you combine, if you split them, and that's what the market does, it helps you split them, it allows you to buy, like, layer on services, but just buy from the market, you can make lots of money. So companies like Modal, who don't own the underlying compute, like they don't own it, lots of money, fantastic product. And then companies like Corbeave, who are functionally like really, really good real estate businesses, lots of money, fantastic product. But if you combine them, you die. That's the economic reality of compute. I think it also splits into trading versus inference, which are different kinds of workloads. Yeah. And then, yeah, one comment about the price sensitivity thing before we leave this. This topic, I want to credit Martin Casado for coining or naming this thing, which is like, you know, you said, you said this thing about like, you don't have room for a 10% margin on GPUs for software. Yep. And Martin actually played it out further. It's his first one I ever saw doing this at large enough runs. So let's say GPT-4 and O1 both had a total trading cost of like a $500 billion is the rough estimate. When you get the $5 billion runs, when you get the $50 billion runs, it is actually makes sense to build your own. You're going to have to get into chips, like for OpenEI to get into chip design, which is so funny. I would make an ASIC for this run. Yeah, maybe. I think a caveat of that that is not super well thought about is that only works if you're really confident. It only works if you really know which chip you're going to do. If you don't, then it's a little harder. So it makes in my head, it makes more sense for inference where you've already established it. But for training there's so much like experimentation. Any generality, yeah. Yeah. The generality is much more useful. Yeah. In some sense, you know, Google's like six generations into the CPUs. Yeah. Yeah. Okay, cool. Maybe we should go into SF Compute now. Sure. Yeah.
Alessio [00:20:37]: Yeah. So you kind of talked about the different providers. Why did you decide to go with this approach and maybe talk a bit about how the market dynamics have evolved since you started a company?
Evan [00:20:47]: So originally we were not doing this at all. We were definitely like forced into this to some extent. And SF Compute started because we wanted to go train models for music and audio in general. We were going to do a sort of generic audio model at some points, and then we were going to do a music model at some points. It was an early company. We didn't really spec down on a particular thing. But yeah, we were going to do a music model and audio model. First thing that you do when you start any AI lab is you go out and you buy a big cluster. The thing we had seen everybody else do was they went out and they raised a really big round and then they would get stuck. Because if you raise the amount of money that you need to train a model initially, like, you know, the $50 million pre-seed, pre-revenue, your valuation is so high or you get diluted so much that you can't raise the next round. And that's a very big ask to make. And also, I don't know, I felt like we just felt like we couldn't do it. We probably could have in retrospect, but I think one, we didn't really feel like we could do it. Two, it felt like if we did, we would have been stuck later on. We didn't want to raise the big round. And so instead, we thought, surely by now, we would be able to just go out. To any provider and buy like a traditional CPU cloud would sell offer you and just buy like on demand or buy like a month or so on. And this worked for like small incremental things. And I think this is where we were basing it off. We just like assumed we could go to like Lambda or something and like buy thousands of at the time A100s. And this just like was not at all the case. So we started doing all the sales calls with people and we said, OK, well, can we just get like month to month? Can we get like one month of compute or so on? Everyone told us at the time, no. You need to have a year long contract or longer or you're out of luck. Sorry. And at the time, we were just like pissed off. Like, why won't nobody sell us a month at a time? Nowadays, we totally understand why, because it's the same economic reason. Because if you if they had sold us the month to month or so on and we canceled or so on, they would have massive risk on that. And so the optimal thing to do was to only to just completely abandon the section of the market. We didn't like that. So our plan was we were going to buy a year long contract anyway. We would use a month. And then we would. At least the other 11 months. And we were locked in for a year, but we only had to pay on every individual month. And so we did this. But then immediately we said, oh, shit, now we have a cloud provider, not a like training models company, not an AI lab, because every 30 days we owed about five hundred thousand dollars or so and we had about five hundred thousand dollars in the bank. So that meant that every single month, if we did not sell out our cluster, we would just go bankrupt. So that's what we did for the first year of the company. And when you're in that position. You try to think how in the world you get out of that position, what that transition to is, OK, well, we tend to be pretty good at like selling this cluster every month because we haven't died yet. And so what we should do is we should go basically be like this broker for other people and we will be more like a GPU real estate or like a GPU realtor. And so we started doing that for a while where we would go to other people who had who was trying to sell like a year long contract with somebody and we'd go to another person who like maybe this person wanted six months and somebody else on six months or something and we'd like combine all these people. Together to make the deal happen and we'd organize these like one off bespoke deals that looked like basically it ended up with us taking a bunch of customers, us signing with a vendor, taking some cut and then us operating the cluster for people typically with bare metal. And so we were doing this, but this was definitely like a oh, shit, oh, shit, oh, shit. How do we get out of our current situation and less of a like a strategic plan of any sort? But while we were doing this, since like the beginning of the company, we had been thinking about how to buy GPU clusters, how to sell them effectively, because we'd seen every part of it. And what we ended up with was like a book of everybody who's trying to buy and everyone is trying to sell because we were these like GPU brokers. And so that turned into what is today SF Compute, which is a compute market, which we think we are the functionally the most liquid GPU market of any capacity. Honestly, I think we're the only thing that actually is like a real market that there's like bids and asks and there's like a like a trading engine that combines everything. And so. I think we're the only place where you can do things that a market should be able to do. Like you can go on SF Compute today and you get thousands of H100s for an hour if you want. And that's because there is a price for thousands of GPUs for an hour. That is like not a thing you can reasonably do on kind of any other cloud provider because nobody should realistically sell you thousands of GPUs for an hour. They should sell it to you for a year or so on. But one of the nice things about a market is that you can buy the year on SF Compute. But then if you need to sell. Back, you can sell back as well. And that opens up all these little pockets of liquidity where somebody who's just trying to buy for a little bit of time, some burst capacity. So people don't normally buy for an hour. That's not like actually a realistic thing, but it's like the range somebody who wants, who is like us, who needed to buy for a month can actually buy for a month. They can like place the order and there is actually a price for that. And it typically comes from somebody else who's selling back. Somebody who bought a longer term contract and is like they bought for some period of time, their code doesn't work, and now they need to like sell off a little bit.
Alessio [00:25:49]: What are the utilization rates at which a market? What are the utilization rates at which a market? Like this works, what do you see the usual GPU utilization rate and like at what point does the market get saturated?
Evan [00:26:00]: Assuming there are not like hardware problems or software problems, the utilization rate is like near 100 percent because the price dips until the utilization is 100 percent. So the price actually has to dip quite a lot in order for the utilization not to be. That's not always the case because you just have logistical problems like you get a cluster and parts of the InfiniBand fabric are broken. And there's like some issue with some switch somewhere and so you have to take some portion of the cluster offline or, you know, stuff like this, like there's just underlying physical realities of the clusters, but nominally we have better utilization than basically anybody because, but that's on utilization of the cluster, like that doesn't necessarily translate into, I mean, I actually do think we have much better overall money made for our underlying vendors than kind of anybody else. We work with the other GPU clouds and the basic pitch to the other GPU clouds is one. So we can sell your broker so we can we can find you the long term contracts that are at the prices that you want, but meanwhile, your cluster is idle and for that we can increase your utilization and get you more money because we can sell that idle cluster for you and then the moment we find the longer, the bigger customer and they come on, you can kick off those people and then go to the other ones. You get kind of the mix of like sell your cluster at whatever price you can get on the market and then sell your cluster at the big price that you want to do for long term contract, which is your ideal business model. And then the benefit of the whole thing being on the market. Is you can pitch your customer that they can cancel their long term contract, which is not a thing that you can reasonably do if you are just the GPU cloud, if you're just the GPU cloud, you can never cancel your contract, because that introduces so much risk that you would otherwise, like not get your cheap cost of capital or whatever. But if you're selling it through the market, or you're selling it with us, then you can say, hey, look, you can cancel for a fee. And that fee is the difference between the price of the market and then the price that they paid at, which means that they canceled and you have the ability to offer that flexibility. But you don't. You don't have to take the risk of it. The money's already there and like you got paid, but it's just being sold to somebody else. One of our top pieces from last year was talking about the H100 glut from all the long term contracts that were not being fully utilized and being put under the market. You have on here dollar a dollar per hour contracts as well as it goes up to two. Actually, I think you were involved. You were obliquely quoted in that article. I think you remember. I remember because this was hidden. Well, we hid your name, but then you were like, yeah, it's us. Yeah. Could you talk about the supply and demand of H100s? Was that just a normal cycle? Was that like a super cycle because of all the VC funding that went in in 2003? What was that like? GPU prices have come down. Yeah, GPU prices have come down. And there's some part that has normal depreciation cycle. Some part of that is just there were a lot of startups that bought GPUs and never used them. And now they're lending it out and therefore you exist. There's a lot of like various theories as to why. This happened. I dislike all of them because they're all kind of like they're often said with really high confidence. And I think just the market's much more complicated than that. Of course. And so everything I'm going to say is like very hedged. But there was a series of like places where a bunch of the orders were placed and people were pitching to their customers and their investors and just the broader market that they would arrive on time. And that is not how the world works. And because there was such a really quick build out of things, you would end up with bottlenecks in the supply chain somewhere that has nothing to do with necessarily the chip. It's like the InfiniBand cables or the NICs or like whatever. Or you need a bunch of like generators or you don't have data center space or like there's always some bottleneck somewhere else. And so a lot of the clusters didn't come online within the period of time. But then all the bottlenecks got sorted out and then they all came online all at the same time. So I think you saw a short. There was a shortage because supply chain hard. And then you saw a increase or like a glut because supply chain eventually figure itself out. And specifically people overordered in order to get the allocation that they wanted. Then they got the allocations and then they went under. Yeah, whatever. Right. There was just a lot of shenanigans. A caveat of this is every time you see somebody like overordered, there is this assumption that the problem was like the demand went down. I don't think that's the case at all. And so I want to clarify that. It definitely seems like a shortage. Like there's more demand for GPUs than there ever was. It's just that there was also more supply. So at the moment, I think there is still functionally a glut. But the difference that I think is happening is mostly the test time inference stuff that you just need way more chips for that than you did before. And so whenever you make a statement about the current market, people sort of take your words and then they assume that you're making a statement about the future market. And so if you say there's a glut now, people will continue to think there's a glut. But I think what is happening at the moment. My general prediction is that like by the winter, we will be back towards shortage. But then also, this very much depends on the rollout of future chips. And that comes with its own. I think I'm trying to give you like a good here's Evan's forecast. Okay. But I don't know if my forecast is right. You don't have to. Nobody is going to hold you to it. But like I think people want to know what's true and what's not. And there's a lot of vague speculations from people who are not that close to the market actually. And you are. I think I'm a closer. Close to the market, but also a vague speculator. Like I think there are a lot of really highly confident speculators and I am indeed a vague speculator. I think I have more information than a lot of other people. And this makes me more vague of a spectator because I feel less certain or less confident than I think a lot of other people do. The thing I do feel reasonably confident about saying is that the test time inference is probably going to quite significantly expand the amount of compute that was used for inference. So a caveat. This is like pretty much all the inference demand is in a few companies. A good example is like lots of bio and pharma was using H100s training sort of the bio models of sorts. And they would come along and they would buy, you know, thousands of H100s for training and then just like not a lot of stuff for inference. Not in any, not relative to like an opening iron anthropic or something because they like don't have a consumer product. Their inference event, if they can do it right. There's really like only one inference event that matters. And obviously I think they're going to run into it. And Batch and they're not going to literally just run one inference event. But like the one that produces the drug is the important one. Right. And I'm dumb and I don't know anything about biology, so I could be completely wrong here. But my understanding is that's kind of the gist. I can check that for you. You can check that for me. Check that for me. But my understanding is like the one that produces the sequence that is the drug that, you know, cures cancer or whatever. That's the important deal. But like a lot of models look like this where they're sort of more enterprising use cases or they're so prior to something that looks like test time inference. You got lots and lots of demand for training and then pretty much entirely fell off for inference. And I think like we looked at like Open Router, for example, the entirety of Open Router that was not anthropic or like Gemini or OpenAI or something. It was like 10 H100 nodes or something like that. It's just like not that much. It's like not that many GPUs actually to service that entire demand. But that's like a really sizable portion of the sort of open source market. But the actual amount of compute needed for it was not that much. But if you imagine like what an OpenAI needs for like GPT-4, it's like tremendously big. But that's because it's a consumer product that has almost all the inference demand. Yeah, that's a message we've had. Roughly open source AI compared to closed AI is like 5%. Yeah, it's like super small. Super small. It's super small. Super small. But test time inference changes that quite significantly. So I will... I will expect that to increase our overall demand. But my question on whether or not that actually affects your compute price is entirely based on how quickly do we roll out the next chips. The way that you burst is different for test time.
Alessio [00:34:01]: Any thoughts on the third part of the market, which is the more peer-to-peer distributed, some are like crypto-enabled, like Hyperbolic, Prime Intellect, and all of that. Where do those fit? Like, do you see a lot of people will want to participate in a peer-to-peer market? Or just because of the capital requirements at the end of the day, it doesn't really matter?
Evan [00:34:20]: I'm like wildly skeptical of these, to be frankly. The dream is like steady at home, right? I got this $15.90. Nobody has $15.90. $14.90 sitting at home. I can rent it out. Yeah. Like, I just don't really think this is going to ever be more efficient than a fully interconnected cluster with InfiniBand or, you know, whatever the sort of next spec might be. Like, I could be completely wrong. But speaking of... I mean, like, SpeedoLite is really hard to beat. And regardless of whatever you're using, you just like can't get around that physical limitation. And so you could like imagine a decentralized market that still has a lot of places where there's like co-location. But then you would get something that looks like SF Compute. And so that's what we do. That's why we take our general take is like on SF Compute, you're not buying from like random people. You're buying from the other GPU clouds, functionally. You're buying from data centers that are the same genre of people that you would work with already. And you can specify, oh, I want all these nodes to be co-located. And I don't think you're really going to get around that. And I think I buy crypto for the purposes of like transferring money. Like the financial system is like quite painful and so on. I can understand the uses of it to sort of incentivize an initial market or try to get around the cold start problem. We've been able to get around the cold start problem just fine. So it didn't actually need that at all. What I do think is totally possible is you could launch a token and then you could like subsidize the crypto. You could compute prices for a bit, but like maybe that will help you. I think that's what Nuus is doing. Yeah, I think there's lots of people who are trying to do things like this, but at some point that runs out. So I would, I think generally agree. I think the only thread in that model is very fine grained mixture of experts that can be like algorithms can shift to adapt to hardware realities. And the hardware reality is like, okay, it's annoying to do large co-located clusters. Then we'll just redesign attention or whatever in our architecture to distribute it more. There was a little bit buzz of block attention last year that Strong Compute made a big push on. But I think like, you know, in a world where we have 200 experts in MOE model, it starts to be a little bit better. Like, I don't disagree with this. I can imagine the world in which you have like, in which you've redesigned it to be more parallelizable, like across space.
Evan [00:36:43]: But assuming without that, your hardware limitation is your speed of light limitation. And that's a very hard one to get around.
Alessio [00:36:50]: Any customers or like stories that you want to shout out of like maybe things that wouldn't have been economically viable like others? I know there's some sensitivity on that.
Evan [00:37:00]: My favorites are grad students, are folks who are trying to do things that would normally otherwise require the scale of a big lab. And the grad students are like the worst pilots. They're like the worst possible customer for the traditional GPU clouds because they will immediately turn if you sell them a thing because they're going to graduate and they're not going to go anywhere. They're not going to like, that project isn't continuing to spend lots of money. Like sometimes it does, but not if you're like working with the university or you're working with the lab of some sort. But a lot of times it's just like the ability for us to offer like big burst capacity, I think is lovely and wonderful. And it's like one of my favorite things to do because all those folks look like we did. And I have a special place in my heart for that. I have a special place in my heart for young hackers and young grad students and researchers who are trying to do the same genre of thing that we are doing. For the same reason, I have a special place in my heart for like the startups, the people who are just actively trying to compete on the same scale, but can't afford it time-wise, but can afford it spike-wise. Yeah, I liked your example of like, I have a grant of 100K and it's expiring. I got to spend it on that. That's really beautiful. Yeah. Interesting. Has there been interesting work coming out of that? Anything you want to mention? Yeah. So from like a startup perspective, like Standard Intelligence and Find, P-H-I-N-D. We've had them on the pod.
Swyx [00:38:23]: Yeah. Yeah.
Evan [00:38:23]: That was great. And then from grad students' perspective, we worked a lot with like the Schmidt Futures grantees of various sorts. My fear is if I talk about their research, I will be completely wrong to a sort of almost insulting degree because I am very dumb. But yeah. I think one thing that's maybe also relevant startups and GPUs-wise. Yeah. Is there was a brief moment where it kind of made sense that VCs provided GPU clusters. And obviously you worked at AI Grants, which set up Andromeda, which is supposedly a $100 million cluster. Yeah. I can explain why that's the case or why anybody would think that would be smart. Because I remember before any of that happened, we were asking for it to happen. Yeah. And the general reason is credit risk. Again, it's a bank. Yeah. I have lower risk than you due to credit transformation. I take your risk onto my balance sheet. Correct. Exactly. If you wanted to go for a while, if you wanted to go set up a GPU cluster, you had to be the one that actually bought the hardware and racked it and stacked it, like co-located it somewhere with someone. Functionally, it was like on your balance sheet, which means you had to get a loan. And you cannot get a loan for like $50 million as a startup. Like not really. You can get like venture debt and stuff, but like it's like very, very difficult to get a loan of any serious price for that. But it's like not that difficult to get a loan for $50 million. If you already have a fund or you already have like a million dollars under your assets somewhere or like you personally can like do a personal guarantee for it or something like this. If you have a lot of money, it is way easier for you to get a loan than if you don't have a lot of money. And so the hack of a VC or some capital partner offering equity for compute is always some arbitrage on the credit risk. That's amazing. Yeah. That's a hack. You should do that. I don't think people should do it right now. I think the market has like, I think it made sense at the time and it was helpful and useful for the people who did it at the time. But I think it was a one-time arbitrage because now there are lots of other sources that can do it. And also I think like it made sense when no one else was doing it and you were the only person who was doing it. But now it's like it's an arbitrage that gets competed down. Sure. So it's like super effective. I wouldn't totally recommend it. Like it's great that Andromeda did it. But the marginal increase of somebody else doing it is like not super helpful. I don't think that many people have followed in their footsteps. I think maybe Andreessen did it. Yeah. That's it. I think just because pretty much all the value like flows through Andromeda. What? That cannot be true. How many companies are in the air, Grant? Like 50? My understanding of Andromeda is it works with all the NFTG companies or like several of the NFTG companies. But I might be wrong about that. Again, you know, something something. Nat, don't kill me. I could be completely wrong. But the but you know, I think Andromeda was like an excellent idea to do at the right time in which it occurred. Perfect. His timing is impeccable. Timing. Yeah. Nat and Daniel are like, I mean, there's lots of people who are like... Sears? Yeah. Sears. Like S-E-E-R. Oh, Sears. Like Sears of the Valley. Yeah. They for years and years before any of the like ChatGPT moment or anything, they had fully understood what was going to happen. Like way, way before. Like. AI Grant is like, like five years old, six years old or something like that. Seven years old. When I, when it like first launched or something. Depends where you start. The nonprofit version. Yeah. The nonprofit version was like, like happening for a while, I think. It's going on for quite a bit of time. And then like Nat and Daniel are like the early investors in a lot of the sort of early AI labs of various sorts. They've been doing this for a bit.
Alessio [00:41:58]: I was looking at your pricing yesterday. We're kind of talking about it before. And there's this weird thing where one week is more expensive of both one day and one month. Yeah. What are like some of the market pricing dynamics? What are things that like this to somebody that is not in the business? This looks really weird. But I'm curious, like if you have an explanation for it, if that looks normal to you. Yeah.
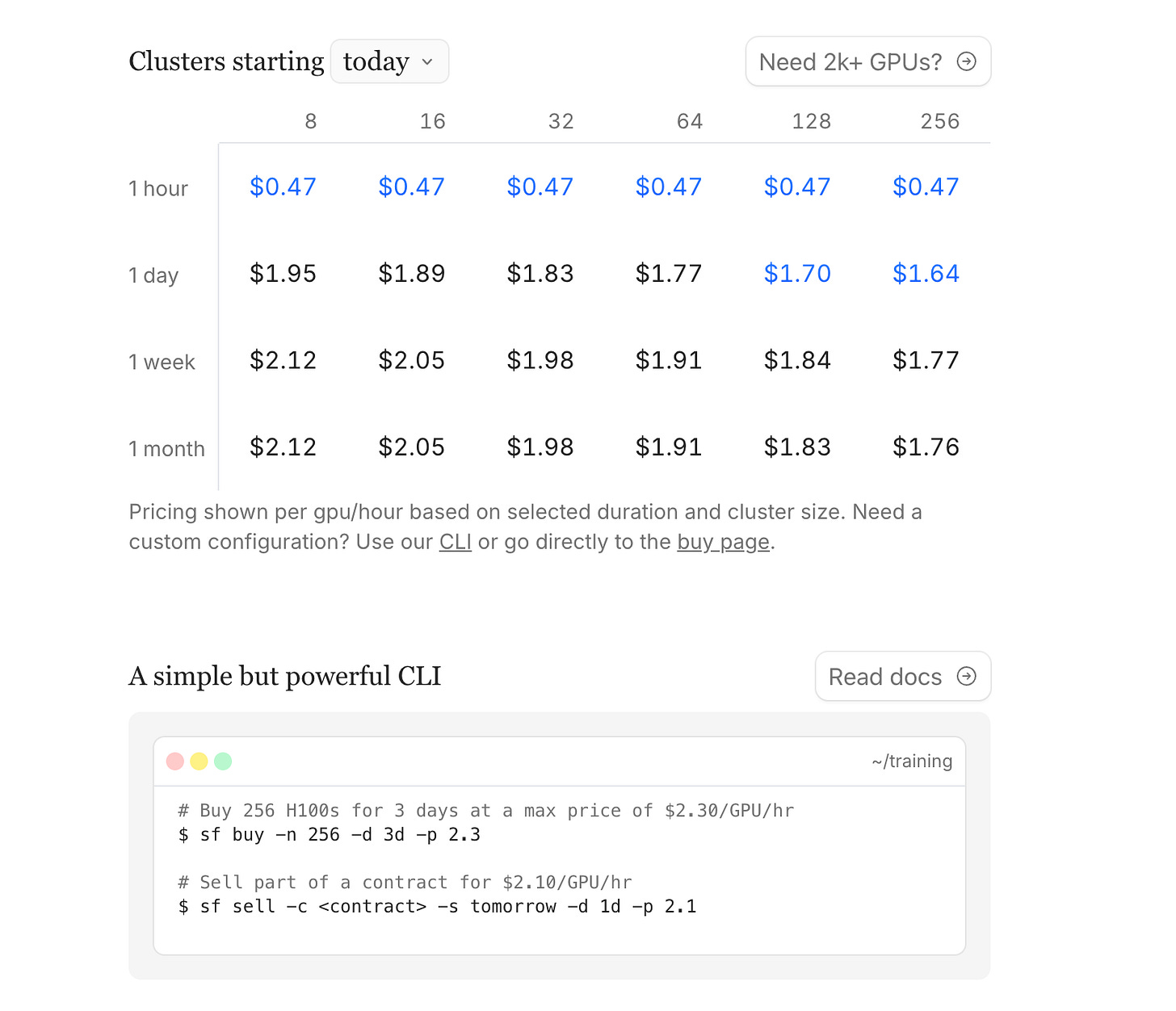
Evan [00:42:18]: So the simple answer is preemptible pricing is cheaper than non-preemptible pricing. And the same economic principle is the reason why that's the case right now. That's not entirely true on SF Compute. SF Compute doesn't really have the concept of preemptible. Instead, what it has is very short reservations. So, you know, you go to a traditional cloud provider and you can say, hey, I want to reserve contract for a year. We will let you do a reserve contract for one hour, which is the part of SFC. But what you can do is you can just buy every single hour continuously. And you're reserving just for that hour. And then the next hour you reserve just for that next hour. And this is obviously like a built in. This is like an automation that you can do. But what you're seeing when you see the cheap price is you're seeing somebody who's buying the next hour, but maybe not necessarily buying an hour after that. So if the price goes up. Up too much. They might not get that next hour. And the underlying part of this of where that's coming from the market is you can imagine like day old milk or like milk that's about to be old. It might drop its price until it's expired because nobody wants to buy the milk that's in the past. Or maybe you can't legally sell it. Compute is the same way. No, you can't sell a block of compute that is not that is in the past. And so what you should do in the market and what people do do is they take. They take a block. A block of compute. And then they drop it and drop it and drop it and drop into a floor price right before it's about to expire. And they keep dropping it until it clears. And so anything that is idle drops until some point. So if you go and use on the website and you set that that chart to like a week from now, what you'll see is much more normal looking sort of curves. But if you say, oh, I want to start right now, that immediate instant, here's the compute that I want right now is the is functionally the preemptible price. It's where most people are getting the best compute or like the best compute prices from. The caveat of that is you can do really fun stuff on SFC if you want. So because it's not actually preemptible, it's it's reserved, but only reserved for an hour, which means that the optimal way to use as of compute is to just buy on the market price, but set a limit price that is much higher. So you can set a limit price for like four dollars and say, oh, if the market ever happens to spike up to four dollars, then don't buy. I don't want to buy that at that price for that price. I don't want to buy that at that price for that price for an hour. But otherwise, just buy at the cheapest price. And if you're comfortable with that of the volatility of it, you're actually going to get like really good prices, like close to a dollar an hour or so on, sometimes down to like 80 cents or whatever. You said four, though. Yeah. So that's the thing. You want to lower the limit. So four is your max price. Four is like where you basically want to like pull the plug and say don't do it because the actual average price is not or like the, you know, the preemptible price doesn't actually look like that. So what you're doing when you're saying four is always, always, always give me this compute. Like continue to buy every hour. Don't preempt me. Don't kick me off. And I want this compute and just buy at the preemptible price, but never kick me off. The only times in which you get kicked off is if there is a big price spike. And, you know, let's say one day out of the year, there's like a four dollar an hour price because of some weird fluke or something. If there are other periods of time, you're actually getting a much lower price than you. It makes sense. Your your average cost that you're actually paying is way better. And your trade off here is you don't literally know what price you're going to get. So it's volatile. But your actual average historically has been like everyone who's done this has gotten wildly better prices. And this is like one of the clever things you can do with the market. If you're willing to make those trade offs, you can get a lot of really good prices. You can also do other things like you can only buy at night, for example. So the price goes down at night. And so you can say, oh, I want to only buy, you know, if the price is lower than 90 cents. And so if you have some long running job, you can make it only run on 90 cents and then you recover back and so on. Yeah. So what you can kind of create as like a spot inst is what other the CPU world has. Yes. But you've created a system where you can kind of manufacture the exact profile that you want. Exactly. That is not just whatever the hyperscalers offer you, which is usually just one thing. Correct. SF Compute is like the power tool. The underlying primitives of like hourly compute is there. Correct. Yeah, it's pretty interesting. I've often asked OpenAI. So like, you know, all these guys. Cloud as well. They do batch APIs. So it's half off of whatever your thing is. Yeah. And the only contract is we'll return in 24 hours. Sure. Right. And I was like, 24 hours is good. But sometimes I want one hour. I want four hours. I want something. And so based off of SF Compute's system, you can actually kind of create that kind of guarantee. Totally. That would be like, you know, not 24, but within eight hours, within four hours, like the work half of a workday. Yes. I can return your results to you. And then I can return it to you. And if your latency requirements are like that low, actually it's fine. Yes. Correct. Yeah. You can carve out that. You can financially engineer that on SFC. Yeah. Yeah. I mean, I think to me that unlocks a lot of agent use cases that I want, which is like, yeah, I worked in a background, but I don't want you to take a day. Yeah. Correct. Take a couple hours or something. Yeah. This touches a lot of my like background because I used to be a derivatives trader. Yeah. And this is a forward market. Yeah. A futures forward market, whatever you call it. Not a future. Very explicitly not a future. Not yet a futures. Yes. But I don't know if you have any other points to talk about. So you recognize that you are a, you know, a marketplace and you've hired, I met Alex Epstein at your launch event and you're like, you're, you're building out the financialization of GPUs. Yeah. So part of that's legal. Mm-hmm. Totally. Part of that is like listing on an exchange. Yep. Maybe you're the exchange. I don't know how that works, but just like, talk to me about that. Like from the legal, the standardization, the like, where is this all headed? You know, is this like a full listed on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange or whatever? What we're trying to do is create an underlying spot market that gives you an index price that you can use. And then with that index price, you can create a cash settled future. And with a cash settled future, you can go back to the data centers and you can say, lock in your price now and de-risk your entire position, which lets you get cheaper cost of capital and so on. And that we think will improve the entire industry because the marginal cost of compute is the risk. It's risk as shown by that graph and basically every part of this conversation. It's risk that causes the price to be all sorts of funky. And we think a future is the correct solution to this. So that's the eventual goal. Right now you have to make the underlying spot market in order to make this occur. And then to make the spot market work, you actually have to solve a lot of technology problems. You really cannot make a spot market work if you don't run the clusters, if you don't have control over them, if you don't know how to audit them, because these are super computers, not soybeans. They have to work. In a way that like, it's just a lot simpler to deliver a soybean than it is to deliver it. I don't know. Talk to the soybean guys. Sure. You know? Yeah. But you have to have a delivery mechanism. Your delivery mechanism, like somebody somewhere has to actually get the compute at some point and it actually has to work. And it is really complicated. And so that is the other part of our business that we go and we build a bare metal infrastructure stack that goes. And then also we do auditing of all the clusters. You sort of de-risk the technical perspective and that allows you to eventually de-risk the financial perspective. And that is kind of the pitch of SF Compute. Yeah. I'll double click on the auditing on the clusters. This is something I've had conversations with Vitae on. He started Rika and I think he had a blog post which kind of shone the light a little bit on how unreliable some clusters are versus others. Correct. Yeah. And sometimes you kind of have to season them and age them a little bit to find the bad cards. You have to burn them in. Yeah. So what do you do to audit them? There's like a burn-in process, a suite of tests, and then active checking and passive checking. Burn-in process is where you typically run LINPACK. LINPACK is this thing that like a bunch of linear algebra equations that you're stress testing the GPUs. This is a proprietary thing that you wrote? No, no, no. LINPACK is like the most common form of burn-in. If you just type in burn-in, typically when people say burn-in, they literally just mean LINPACK. It's like an NVIDIA reference version of this. Again, NVIDIA could run this before they ship, but now the customers have to do it. It's annoying. You're not just checking for the GPU itself. You're checking like the whole component, all the hardware. And it's a lot of work. It's an integration test. It's an integration test. Yeah. So what you're doing when you're running LINPACK or burn-in in general is you're stress testing the GPUs for some period of time, 48 hours, for example, maybe seven days or so on. And you're just trying to kill all the dead GPUs or any components in the system that are broken. And we've had experiences where we ran LINPACK on a cluster and it rounds out, sort of comes offline when you run LINPACK. This is a pretty good sign that maybe there is a problem with this cluster. Yeah. So LINPACK is like the most common sort of standard test. But then beyond that, what you do is we have like a series of performance tests that replicate a much more realistic environment as well that we run just assuming if LINPACK works at all, then you run the next set of tests. And then while the GPUs are in operation, you're also going through and you're doing active tests and passive tests. Passive tests are things that are running in the background while somebody else is running, while like some other workload is running. And active tests are during like idle periods. You're running some sort of check that would otherwise sort of interrupt something. And then the active tests will take something offline, basically. Or a passive check might mark it to get taken offline later and so on. And then the thing that we are working on that we have working partially but not entirely is automated refunds, which is basically like, is the case that the hardware breaks so much. And there's only so much that we can do and it is the effect of pretty much the entire industry. So a pretty common thing that I think happens to kind of everybody in the space is a customer comes online, they experience your cluster, and your cluster has the same problem that like any cluster has, or it's I mean, a different problem every time, but they experience one of the problems of HPC. And then their experience is bad. And you have to like negotiate a refund or some other thing like this. It's always case by case. And like, yeah, a lot of people just eat the cost. Correct. So one of the nice things about a market that we can do as we get bigger and have been doing as we can bigger is we can immediately give you something else. And then also we can automatically refund you. And you're still gonna experience it like the hardware problems aren't going away until the underlying vendors fix things. But honestly, I don't think that's likely because you're always pushing the limits of HPC. This is the case of trying to build a supercomputer. that's one of the nice things that we can do is we can switch you out for somebody else somewhere, and then automatically refund you or prorate or whatever the correct move is. One of the things that you say in this conversation with me was like, you know, you know, a provider is good when they guarantee automatic refunds. Which doesn't happen. But yeah, that's, that's in our contact with all the underlying cloud providers. You built it in already. Yeah. So we have a quite strict SLA that we pass on to you. The reason why I'm like, hedging on this is because we have some amount of active checks, we have some amount of passive checks. There are always new genres of bullshit, and the new genres of bullshit might cause a customer to have bad experience. And the active or passive checks didn't catch it. And so then it's a manual process after that. Then we have like a literal thing in our website that you can just say, Hey, some hardware problem, please tell us. And then we will go and resolve it for you. How, I mean, cards don't change generation to generation. What is a new genre of bullshit? If every component piece in the cluster has maybe like a one in a hundred chance of failing, or maybe a one in a thousand chance of failing, or maybe one in 10,000 chance of failing, You discover them. You discover them. So there's ones that like maybe nobody saw, maybe you didn't see, or maybe only matters for this one cluster with this motherboard in this particular data center or something. There's new interactions that otherwise don't happen. Most problems are really common and you can adapt to them. Like, like a GPU falls off a bus is like one of the most common things that can happen. So it's not SF Compute's job to go fix those things. No, it totally is to some extent. Totally is to some extent. So we, we operate the cluster. So unlike a reseller, which is what we were doing before. Yeah. In almost all cases, we have BMC access. So if on your laptop, there's like the button in the top right hand corner that you can hold down to like re-image the machine, there's a similar thing in like server X that you is like this other box that kind of plugs in and it basically lets you reset the machine from outside. And it's like remote, it's a remote hand sort of thing. So we ask for this and we get this from a lot of our vendors, which means we have quite a lot of ability to solve problems for customers in a way that you might not actually get from a reseller. Oftentimes we are the person who's debugging your cluster. For most customers that we work with, we have Slack channel. Our entire engineering team gets put in the Slack channel. If there was a problem at 2am, we are the ones who are debugging your problem at 2am. Not always the case because we don't physically run the hardware cluster or like the data center itself, but most problems are solvable through this. So that's the auditing side. The other side is I think of a standardization or whatever you call it. Beyond auditing. The other part of the work is kind of standardizing the commodity contracts. Yeah. So there's two ways that we do that. One is that you set like a this or better list. So you set like a spec list and you say, oh, you're going to get like a common variability is the amount of storage on the cluster. And so you'll say like, oh, you're going to get X or better. And there's some guarantee minimum and sometimes you might get more. And then we're working on a persistent storage layer that might sort of abstract a lot of this way, but mostly it's that. And then there's like a white list of motherboards and various things. Genres of things. But the other part is we run the clusters from bare metal up. And so we make a thing that's this like it's a UEFI shim. And if you're not familiar with what UEFI is, a UEFI is like the sort of firmware modern version of BIOS. Modern meaning it's been around for like forever. But you know, BIOS is like really old. It's like this whole IBM thing. And you can write code that exists at the UEFI layer. And again, when you hear UEFI, you should think BIOS. And it does the same sort of thing. It does the same thing as a Pixie boot, but in environments in which Pixie boot doesn't necessarily always work for us. So it basically sits at your BIOS, downloads an image, boots into an image that's like custom for the user. And then on top of that image, we can throw Kubernetes on it. We can throw VMs on it or whatever you want. And at some point, we'll probably like do more stuff with that. But that's functionally what we can do. The nice thing, though, is that because you control from that layer, you can easily image an entire cluster. You make it all the same. You can run your performance tests all automated. So much nicer. Right. Than what we used to do. Yeah. I mean, that is a very important work. I think like for me, as a trader, I need standard contracts. And so there basically needs to be the safe of a GPU. Yes. What we functionally do is we have a market under the hood that is focused on the buyer and the seller, and it's optimized for them. And then beyond that, for a trader, you can standardize around a certain segment of it. And you can trade on that contract. That's the goal that we're trying to get to. But you start by making something that works really well for buyers and really well for sellers. For those who are not familiar with derivatives markets, I can go ahead and say this because the point of being cash settled, which is something that you mentioned, which I think people might miss, is that you don't have to take physical delivery of the GPUs. Right. And so it's a pure financial instrument, which actually does mean that almost for certain, there will be more volume on SFC's marketplace than actually change hands in GPU terms. To be super clear. We are not a derivatives market. This doesn't happen yet. Yeah. We are not a derivatives market. We may in the future work to create a cash settled future. We are not currently a derivatives market. We are an online spot market. Yeah. I just think like people, normies get really upset when they're like, then they learn things like, oh, like derivatives on mortgages are like 12 times larger than the mortgages themselves. Yes. Yeah. No, I, um, a common thing that people have talked to us about, or like a fear or concern, I think people have is like, oh, you're financializing. Compute. And this will like cause various problems of sorts. Subprime crisis. Yeah. Um, and I think, so first I think part of this is just because crypto caused a lot of people to think about finance in the like very de-gen way for the right word. Um, and then before that, um, the sort of 2008, 2009 crisis, um, caused people to think about it also in sort of like a de-genny way. And this is very much not our mindset. The reason to create a derivative at all, or the reason to create a future at all is a risk reduction thing. Um, that's what futures do. The reason why a farmer wants a future is because they have no idea what the weather is going to do. And they don't want to be on the hook, um, for like they have small margins and if things go wrong, they really, really want to have a locked in price. Um, so that way they can like continue to exist for the next year. Data centers are the same way. The way that they solve it today is you go out and you sign long-term contracts with your customers. What that does for you is it means your business is de-risked. Um, you don't have to worry about the revenue for the next year. But that means that the customer now has to worry about what they're going to do with all this compute. And if they don't optimally use it and so on and so on, and that just pushes everything onto the startups who then in turn, push it on to VCs. And so what the VCs are forced to do in order to invest in AI is they have to go and write big, giant valuations, like pre-revenue at ridiculous multiples. So what you've done by not having a future is you've inflated the venture capital market, and that is a bubble. That's totally going to pop. At some point, like a lot of the companies are not going to work and the valuations are not going to work. And what's going to happen is a lot of these funds aren't going to return back to their LPs. And that affects the broader market. The way that you solve that, the way that you add security to the entire economic system in this chain is you add a future. That's how we did it in lots of other markets. It doesn't have to be this like, oh my gosh, we're going to like speculate on GB prices and like whatever. No. The whole point of SF Compute is to reduce the risk. Reduce the technical risk. Reduce the financial risk. Let's just chill out a little bit. There's so much other random shit. It's supercomputers. There's AGI, whatever. No. Let's just like chill the fuck out. I mean, also like Dan is going, raising like at a $30 billion valuation for Ilya, you know, like. Yeah. If everybody else in all of AI is like pushing the hype and the extreme, everything we've been trying to do is go the other way. Like whole website is just like a fucking single page. Um, like the entire brand is just like, what if we were? We're like calm in nature. And then everything that we do as the product is just calm. What if we, what if we were the opposite force of the big hypey extreme thing? What if we just like chilled things out? And part of that was because we, in the beginning were at the whim of the hypey nature. Like our entire origin is every 30 days and we don't sell out, we're going to go crazy and just completely bankrupt the company. And so everybody in the company is just like, what if we just chilled out? What if, what if we stopped? Yeah. This is the first time I've ever heard derivatives are the way to chill out. Yes. No. Futures are the way to chill out. Futures are the way to chill out the entire industry. And um, we wouldn't be doing this if it wasn't that case. I like that.
Alessio [01:01:20]: You have a very nice brand with a, you know, clear sky. We have to ask about the website. Yeah. What was the inspiration behind it? Why did you not go the black neon, more cool thing and go the more nature?
Evan [01:01:33]: I don't think I really am a black neon sort of person. I say. I'm wearing black pants and I thought I was wearing a black shirt, but apparently I'm not. So, um, the actual, the actual thing was a lot of companies do this thing where they, their website, you go to there and it's like a magical experience and like everything is extreme and amazing and credible and then you go to the product and it's like some SaaS app or something. Um, and it's like not actually that exciting. And that expectation of being like really, really good. And then the fall off the drop of not being really, really good. Yeah. It's something that from a product perspective, I never want it to happen, especially because in the beginning, like our product was really bad. And so I don't want to set the expectation that it's going to be like an amazing experience. I want to set the expectation that it's going to be like a good price for short term bursts. And so what we did instead is we set the thing to be really low. You set your expectations really low and then you get a supercomputer for like millions of dollars cheaper than you would have otherwise gotten your supercomputer. And so you have the opposite expectation. You have like really low expectations that are like mild or met higher. Yeah. And I think that's like the correct way to do things. But also I think we were just like so sick of hype and excitement and, um, I just like really want to like not do that. It's weird. Like by, by being anti-hype, you have created hype. Like I would say like the, the, the, the, the vibes are immaculate, you know, like you just, you go to like at the, the bay, the Cal trade, you just put up like a banner. This just, just says SF compute. True. That banner was created about five minutes before we had to actually put something up like before the deadline was there. Yeah. So it opens up Microsoft word and you did some serif. What is the font? Exactly. I don't know. Yeah. That was, um, indeed. Um, the, yeah, I think every time we tried to do the, the only caveat to this, the only caveat that we ever violate this rule with, uh, is when we're pitching San Francisco, I think San Francisco is amazing. So sometimes you will see these like advertisements from the city. Yeah. The city. Um, so if there's a part of San Francisco computes brand, which are these beautiful like images of SF. Yeah. And I am the complete opposite about this. I am such a San Francisco promoter that any time we talk about the city, I want to show the city from the like eyes that we have, which is mostly just gorgeous, beautiful area with nature. Like a lot of people think about San Francisco and they think about like tech industry or they think, yeah, or the tenderloin or something like grind culture or something. And no, like I think about like the fog, um, and just like the gorgeous view over the bridge and just the fact that there is this like massive amount of optimism in the city. And it's the backdrop of that optimism is the most beautiful countryside in all of the world. And so anytime we talk about SF, you will see like, or like we have a billboard somewhere that's just like local friendly supercomputer or whatever. And then the backdrop is like beautiful and amazing. And that's because to some extent we're pitching the city and the people here. And I think that people in the city here are actually really amazing. And so you get to earn the brand. Um, cause the expectations are met. Whereas I think on our own product, I'm typically want it to be better. And so I set the brand a lot lower. Um, and then the expectations are higher. Um, and you still meet the expectations, but you, you set them a little lower. I know. Are you the designer? I know you have an artistic side. Um, so, uh, I was in the beginning, so, uh, I'm like a figurative artist, so I draw people. Um, but we've worked with a design firm. Airfoil was really excellent with us. And then, um, nowadays though, John Pham, um, had a design from Vercel. Yeah. John is unbelievably amazing. Yeah. Um, I think the amount of care and craft and attention to detail that he puts into just everything is so cool. Yeah. Um, like if you go on our buy page right now, you go to sfcompute.com slash buy. There is an Easter egg there that will, you should find. I almost don't want to spoil it, but you should go find that Easter egg. If you just like hover the mouse around the thing in the top right hand corner, um, you will, you'll find it. Yeah, tweet at Evan if you find it. And then the, um, other person is, um, Ethan Anderson, our COO, who, um, has this really, really cool design. He has a RISD design background. And so, uh, his, like, uh, he used to be sort of industrial designery. I'm probably going to say that wrong. He's probably not an actual industrial designer, but design background, same. So I think between me and John and, uh, Ethan, um, I think we. The source of the vibes. The source of the vibes. I had to ask. Yeah. Okay. So we're going to zoom out a little bit. One of the last things I wanted to ask you was actually like, I remember, I think the first time that you was in like kind of cello and you were working on your email. Oh yeah. Yeah. Yeah. And I have a favorite pet topic of mine. We were here with Dharmesh yesterday talking about someone, build an agent that reads my emails. Yeah. And you did. And I think I actually paid for the first one. You were, you were so excited in the early GPT three days. I was like, you were like, uh, I'm building the most expensive startup ever. Yeah. It's so expensive. Anyway. So the point being what I'm trying to get to is you are a very smart guy. You built email. You, you didn't like it. You pivoted away. I've seen other, like every year there's someone who is like, I will crack email. Yeah. And I'll, and then, and then they give up. Yeah. What is so hard about email? I didn't pivot away because the product or the idea was bad. I pivoted away because I was super burnt out. I did a startup for like four years. And the first thing didn't work out. Is this room service? Yeah, this is room service. So my startup before this originally started as Quirk, which was like a mental health app, but then Quirk had the same problems that basically every mental health app has, which is like your retention goes to zero if you work at in any capacity. And so switched and then said, okay, well I will do something that's closer to my actual background was like a distributed systems company called Room Service. Room Service went for about nine months and then sort of had the same problem that I think every other competitor Room Service has, which is mostly people building a house. And so then I went back to our investors at the time, which was Nat and Daniel and specifically Daniel told me that I should go stare at the ocean. And you know, I will find something else to do and just throw shit at the wall. And then I think, I think it was Gustav at YC. Maybe it was probably actually Dalton Caldwell. Dalton Caldwell, like just said, don't die. Like you can just keep doing things and don't die. And so I think I just got it in my head that you should just like keep trying things and not die. And I really, really, really did not want to die and didn't really know what to do. And so I just threw out like 40 products with the assumption that if you just keep trying things, you won't die. This is actually not the most ideal thing to do. You actually should totally just pick a thing and go with it. But my brain wasn't set on like, oh, I should do this particular thing. It was set on not die. And so I just kept going for a very long time for like four years. And by the end of it, I think I was just super burnt out. And I was going to do the email thing with one co-founder and then they quit. And then I was going to do an email thing with another co-founder. And then they fell in love and decided to go get married and you know all that. Okay. So it wasn't that email is intractable. I'm just trying to figure out like, look, is there something bad? Like, is this a graveyard of ideas, right? Everyone wants to do email and then nobody does because something. And I think it's just hard to make an email client. I think it's hard to make an email client. That is, it's a competitive space in which there are lots of things. I do think that the better version of that is something that looks closer to what Intercom is doing. And Intercom obviously existed beforehand. So you can think about like any product. Like, should you be doing it or should somebody else in the industry who already has the existing customer set do it? And I think Intercom has pretty much very successfully done like they already had the position to do it. Like, what do you actually need the AI to write your emails for? Like, most people don't need this. But what who does need this is like support use cases is pretty much there. And the people who are best able to execute on this is totally Intercom. So like props to Owen. I think that was like completely the correct move. Yeah. Closing thoughts. Call to action.
Alessio [01:09:07]: Yes. Oh, yeah, we are.
Evan [01:09:09]: We are hiring for two roles as of this recording. I don't know. Maybe this will change and we'll be hiring for different roles. So go to the website or whatever. But the first role is for traditional systems engineering. This is like low level systems or low level Linux systems. Yeah. So I'll rest most all of our code bases and rest. But we're not necessarily just looking for like rest engineers. We're specifically looking for like Linux people sort of pitches. You get to work on supercomputers. You get to work on one of the few places in supercomputers that I think has a pretty good business model and is like a like a working thing. And people generally seem to think that our vibe as of compute is very nice. The we have just an unbelievable. Excellent team. I think nowadays our CTO is Eric Park. He's the co-founder of Voltage Park, which is one of the other GPU clouds. And he is quite possibly the sweetest man I've ever met. He is extremely chill and also just extremely earnest and kind. And the rest of the team kind of feels that energy very strongly. And then the other role that we're hiring for is financial systems engineering, which I really should learn what it's not systems engineering, but we should really find a better name for this role. It's basically a fintech engineer. That it's we have the same problems as traditional fintech does. And that's like we have a ledger. We have recording requirements and all that stuff. This role is responsible for the not lose all the money. Cool. Like, we've got a whole bunch of money flowing through us. There is a bunch of stuff that you need to do in order to not lose all that money. And then the actual outcome of that work, besides not just losing all the money, which is very important, is that you end up with better prices for the vendors and better prices for the buyers. And this means that your grad student who is an engineer. Who is making the cancer cure or whatever and needs to be able to buy like 100K of compute to like scale up really big actually can do so. And that's I think the like this is part of the reason to work at SFC is that you're the things you do actually matter in a way that doesn't necessarily always at all the companies functionally. We run supercomputers like not soybeans or I don't know. It's a very cool place to work because your outcomes of what you do have real deal impact in a way that you don't always get when you're doing SaaS. Excellent pitch. I bet you've done that a lot, but it's nice to hear for the first time. I was going to say, like, you know, have you looked into Tiger Beetle, the dual entry accounting database? We have. That seems to be the thing if you want to make systems that don't lose money. Yes. Systems that don't lose money. There are lots of other things you have to do. Like you have to make things in a format that your accountants can read and then get audited and so on. It's not purely just the yeah, it's not purely just the tech. Cool. Awesome. Thank you so much. Of course.